What are the applications of permanent mold casting?
December 12, 2025
Permanent mold casting is a highly efficient and versatile manufacturing process that has gained traction across various industries. By utilizing durable, reusable molds, this casting technique offers a unique blend of precision and repeatability, making it an ideal choice for producing high-quality aluminum components.
In this article, we will explore the diverse permanent mold casting applications, delving into its principles, benefits, and specific use cases across different sectors.
What is permanent mold casting?
Permanent mold casting is a metal casting process that involves pouring molten metal into a reusable mold made from materials such as steel or iron. This method is known for producing components with excellent dimensional accuracy, smooth surface finishes, and consistent mechanical properties. The key principles include:
Durability
Permanent molds can withstand multiple casting cycles without significant wear.
Material Variety
Permanent mold casting materials most commonly include aluminum and zinc alloys, which are favored for their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
Heat Conductivity
The metal molds provide efficient heat transfer, allowing for quicker cooling and solidification of the molten metal.
The advantages of using permanent molds over other casting types include reduced production costs over time, improved part consistency, and enhanced mechanical properties of the finished product. Additionally, Procast employs advanced simulation techniques, such as Solidification Analysis, to eliminate defects before production, ensuring that components meet stringent quality standards from the outset.
What are the applications of casting processes?
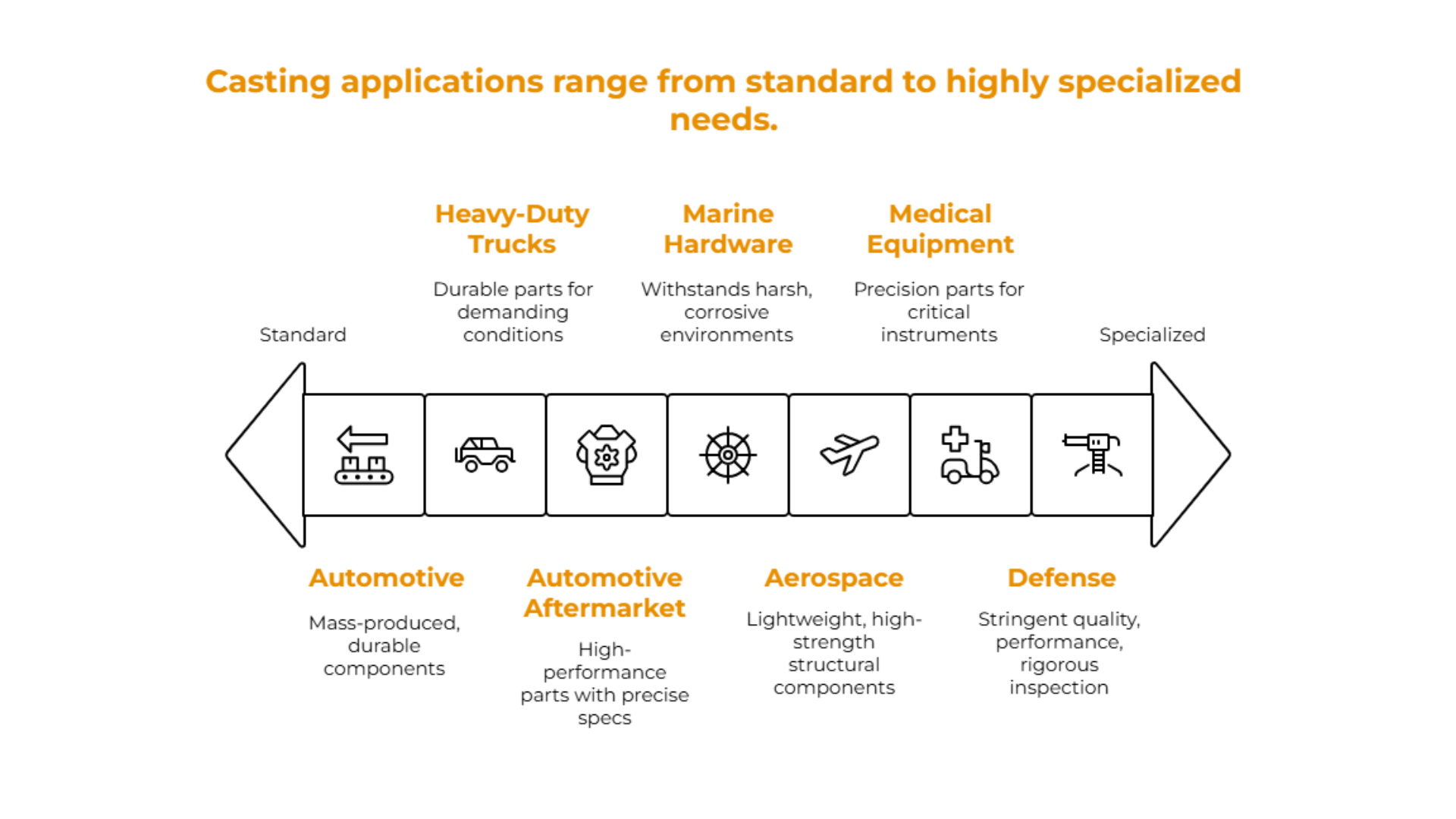
Casting processes are integral to various manufacturing sectors, with permanent mold casting being particularly prominent in specific applications. Industries that extensively utilize casting processes include:
- Automotive: Components such as engine blocks and transmission housings.
- Aerospace: Structural components and housings for engines.
- Medical Equipment: Precision parts for surgical instruments and devices.
- Heavy-Duty Trucks: Structural and functional parts require high durability.
- Specific permanent mold casting examples include:
- Automotive Aftermarket Parts: High-performance components that require precise specifications.
- Marine Hardware: Components that must withstand harsh environments.
- Defense: Parts that require stringent quality and performance standards, often subject to rigorous CMM inspection to ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Permanent mold casting stands out as a reliable and efficient process for producing high-quality, durable components across multiple industries. Its ability to deliver precise dimensions, consistent quality, and superior mechanical properties makes it a preferred choice for applications where performance and longevity are critical. From automotive to defense, the versatility of this casting method continues to drive innovation and excellence in modern manufacturing.
What is an example of expendable mold casting?
The expendable mold casting process is differentiated by the mold being made from materials that cannot be reused after the casting is complete. This method allows greater geometric complexity than permanent mold casting, though it typically involves higher costs and longer production times. Examples of expendable mold casting processes include:
- Sand Casting: A widely used method for large components.
- Investment Casting: Ideal for intricate designs and high-precision parts.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Complex Shapes: Ability to create intricate designs that may not be feasible with permanent molds.
Material Versatility: Can accommodate a wide range of metals. |
Higher Costs: Due to the need for new molds for each production run.
Longer Lead Times: More time is required for mold creation and setup. |
What are the advantages and disadvantages of permanent mold casting?
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency: Reduced costs in high-volume production due to reusable molds.
Improved Quality: Enhanced dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Reduced Waste: Less material wasted compared to expendable molds. |
Initial Investment: Higher upfront costs for mold creation.
Limited Complexity: Less flexibility in mold design compared to expendable methods. |
When compared to other methods, permanent mold casting stands out for its balance of cost, quality, and efficiency, making it a preferred choice in many manufacturing scenarios. Additionally, Procast’s in-house engineering and tooling design and manufacturing capabilities ensure that every project benefits from a seamless, all-in-one solution, further enhancing permanent mold casting’s advantages.
Types of permanent mold casting and their applications
There are several types of permanent mold casting techniques, each suited for specific applications:
- Tilt-Pour Casting: Ideal for producing intricate shapes, this method involves tilting the mold to allow the molten metal to flow in with reduced turbulence.
- Tatic Pour Casting: Also for producing intricate shapes and involves pouring the metal into a stationary mold which utilizes the gating system to control the pouring process
Materials used in each type include:
- Aluminum Alloys: Commonly used for lightweight applications.
- Zinc Alloys: Preferred for their corrosion resistance, added strength, and smaller features.
Ready to explore the benefits of permanent mold aluminum casting?
Dive deeper into our expert insights and real-world applications that can elevate your manufacturing process here at Procast Technologies. Discover how Procast’s innovative techniques can transform your production today!
