The Permanent Mold Process: Advantages and Disadvantages?
December 12, 2025
The casting process is a fundamental manufacturing technique that enables the creation of complex, high-precision components. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of the casting process is critical for industries that rely on high-quality components, such as automotive, medical, and defense sectors. This article will explore the various types of molds, the applications of permanent mold casting, and the benefits and drawbacks associated with this manufacturing method.
What Are the Two Types of Molds in Casting?
In casting, two primary mold types define the process: permanent molds and expendable molds.
Permanent Molds
Made from durable materials such as steel or iron, these molds can be reused multiple times. They are ideal for high-volume production runs and are often used in processes like Permanent Mold Aluminum Casting.
✓Lower long-term costs due to reuse
✓Improved dimensional accuracy
✓Better surface finish
✓Enhanced efficiency through in-house engineering that optimizes each mold for its specific applications
✓Integration of advanced simulation techniques, such as Solidification Analysis, to predict and reduce defects
Expendable Molds
Typically made from sand or plaster, these molds are used for single casting cycles. Once the casting is complete, the mold is destroyed to retrieve the part.
✓Flexibility in producing intricate designs
✓Lower initial setup costs for small production runs
✓Compatibility with a wide range of materials
✓Integration of advanced simulation techniques, such as Solidification Analysis, to predict and reduce defects
Understanding these types of casting methods is essential for selecting the right approach based on production volume, material requirements, and desired precision.
What is permanent mold casting used for?
Permanent mold casting is primarily used for producing aluminum and zinc alloy components. The process involves pouring molten metal into a pre-heated mold, allowing it to solidify and take shape.
Industries that commonly prefer this method include:
The use of permanent molds ensures high dimensional accuracy and a superior surface finish, making it a preferred choice in highly regulated sectors. Our in-house tooling design and manufacturing capabilities further enhance the reliability and performance of the cast components.
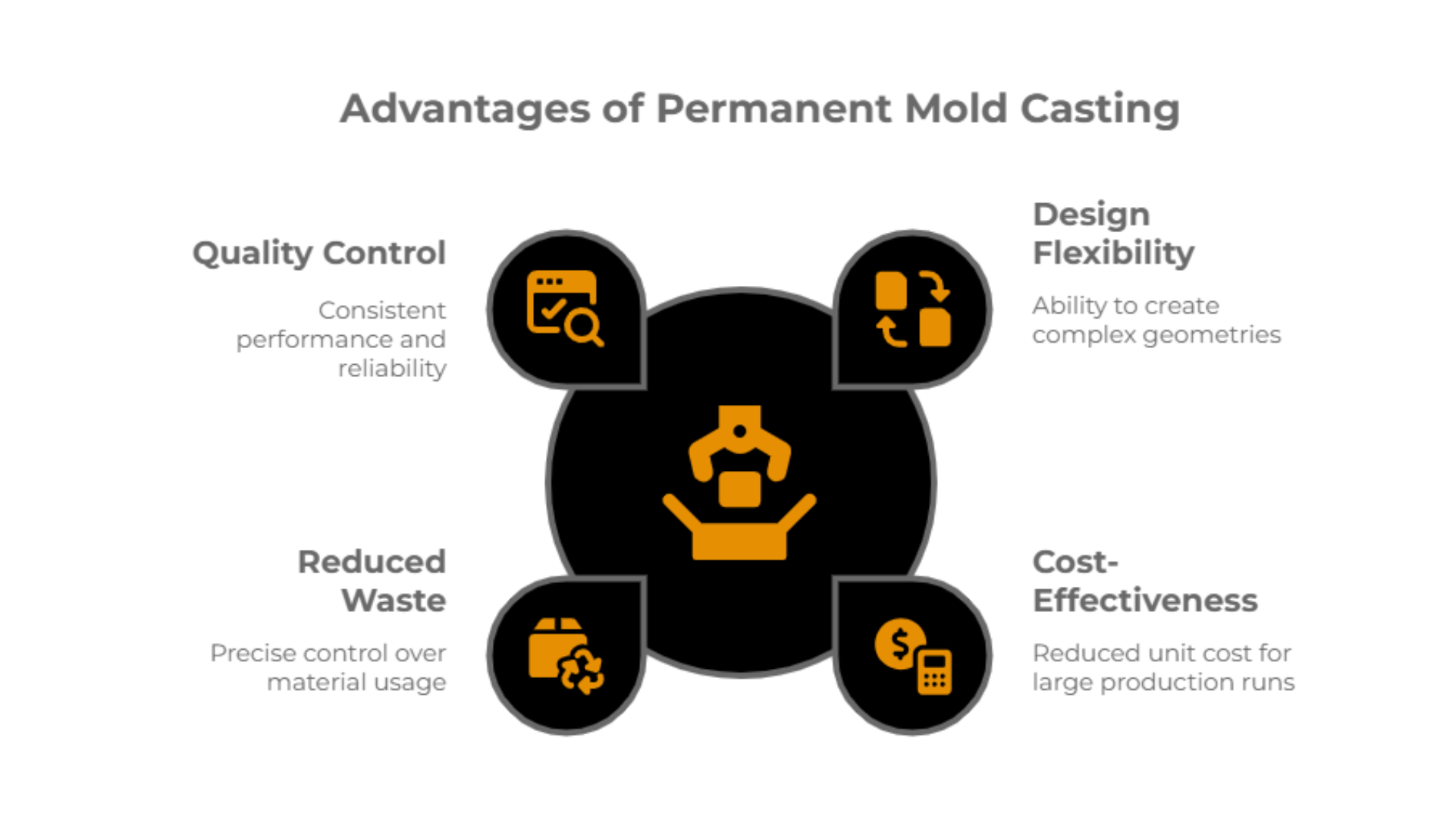
What are the advantages of the Permanent Mold casting process?
The casting process offers several key advantages that make it a widely used method in modern manufacturing. Understanding these benefits—along with the unique trade-offs of sand casting—helps manufacturers select the most efficient method for their specific applications.
Design Flexibility: Casting enables the production of complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods.
Cost-Effectiveness: For large production runs, the cost per unit decreases considerably as initial setup expenses are distributed across many parts.
Reduced Waste: Casting minimizes material waste by allowing precise control over the volume of molten metal poured into each mold.
Quality Waste: With ISO 9001:2015-certified processes, quality assurance with the permanent mold process is maintained at every stage, ensuring consistent performance and reliability.
These strengths—particularly when weighed against the advantages and disadvantages of sand casting—demonstrate why Permanent Moldcasting remains a crucial technique for achieving high-quality, cost-effective production across various industries.
What are the common disadvantages of the casting process?
Despite its advantages, the casting process can produce defects that may impact product quality. Some typical defects include:
By identifying and addressing these common defects of the casting process, manufacturers enhance product quality and reliability.
Elevate Your Manufacturing Process
For more insights into Permanent Mold Aluminum Casting and to learn how Procast can elevate your manufacturing processes, visit our website. Discover how our expertise, wide range of services, and advanced technologies can help meet your unique casting and machining needs. Let Procast be your trusted partner in achieving high-quality, reliable components for your industry!
