Permanent Mold Casting Advantages and Disadvantages
December 12, 2025
In the realm of aluminum casting, permanent mold aluminum casting stands out for its efficiency and precision. It combines the benefits of traditional casting with modern technology, making it a preferred choice for many industries. In this article, we will delve into the advantages and disadvantages of permanent mold casting, helping you understand how this process can impact your manufacturing needs.
What is Permanent Mold Casting Used For?
Permanent mold casting is a process that utilizes reusable molds to create metal parts. This technique is primarily used for producing high-quality, complex shapes with superior dimensional accuracy.
Permanent mold casting is particularly beneficial for high-volume production runs where consistent quality is crucial. It is especially advantageous for components with intricate designs and tight tolerances, which are common in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical.
This casting method is particularly valued in industries where the final product must undergo additional processing. In the aerospace industry for example, after parts are cast using permanent mold casting, they often undergo specialized thermal treatments to improve material properties such as toughness and fatigue resistance. This added flexibility makes the method well-suited for producing components that not only are highly precise but also have the necessary strength for demanding environments.
Advances in simulation software now allow manufacturers to model and simulate the entire casting process, optimizing cooling rates and mold designs to reduce defects such as shrinkage or porosity. This makes permanent mold casting increasingly valuable for producing lightweight, high-strength parts with minimal waste, further driving its adoption in industries requiring precision and durability.
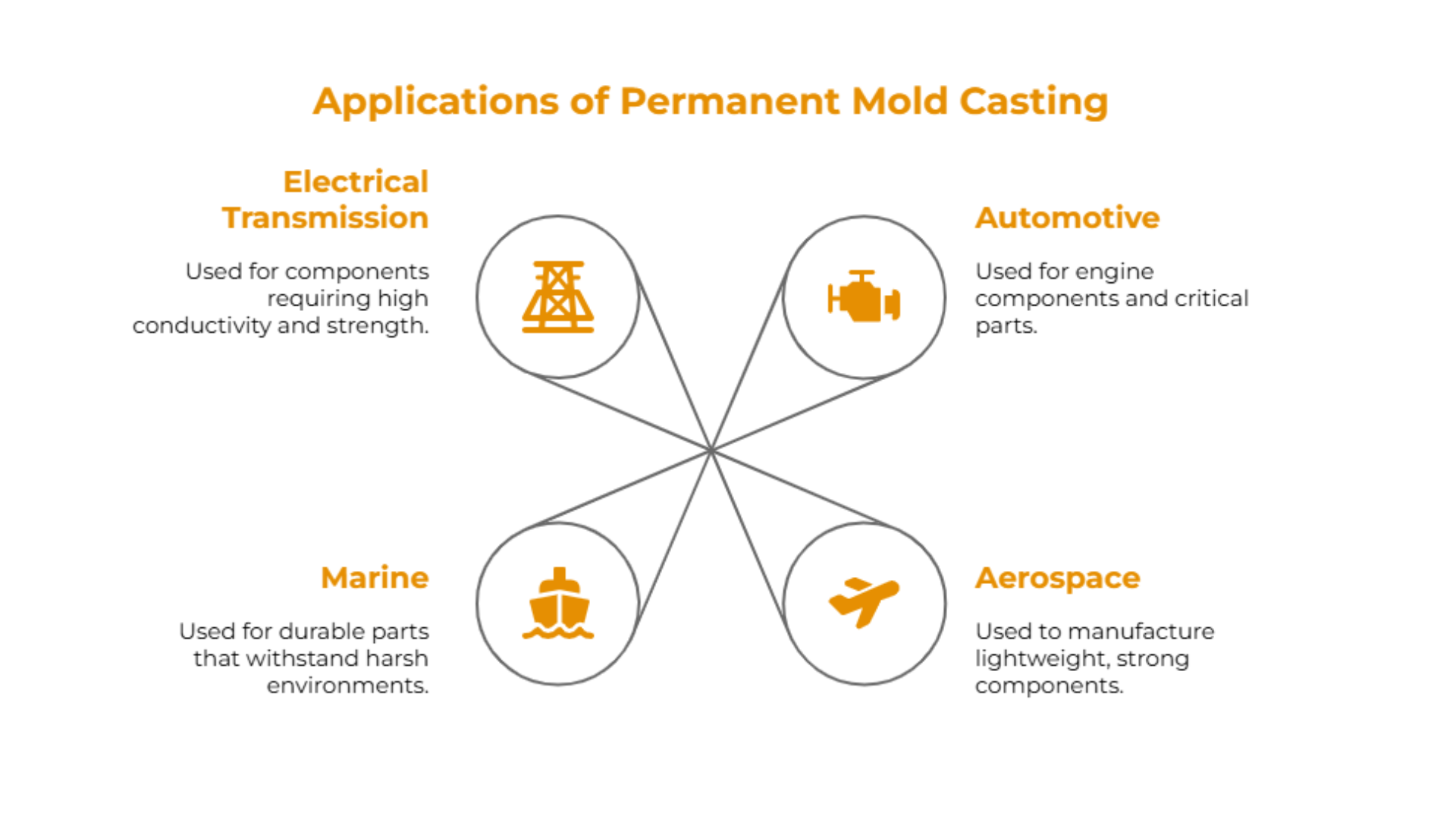
Industries that commonly utilize this method include:
| Automotive: For engine components and other critical parts. | Aerospace: To manufacture lightweight, strong components. |
| Marine: For durable parts that withstand harsh environments. | Electrical Transmission: For components requiring high conductivity and strength. |
Examples of permanent mold casting applications include engine blocks, housings, and intricate brackets that require both strength and precision. Additionally, the permanent mold process is particularly advantageous for high-volume production runs, where consistency and quality are paramount.
Why is Permanent Mold Casting Used?
The popularity of permanent mold casting can be attributed to several key benefits:
1.Efficiency: The reusable nature of the molds allows for faster production cycles. This efficiency is further enhanced by our complete equipment ecosystem, including ERP (Jobb Boss) and MES (AMPER), which facilitate real-time production monitoring and workflow optimization.
In addition to its efficiency, permanent mold casting can produce parts with more intricate internal features, which might be difficult or impossible to achieve with other casting methods like pressure diecasting.
Permanent mold casting further excels at creating complex geometries, such as internal passages or thin-walled sections. This makes it highly suitable for industries where part complexity is essential, such as the production of aerospace engine components or medical components.
Furthermore, improvements in automation and process monitoring are increasing production speed and reducing human error. Automated systems allow real-time adjustments during the casting process, improving the overall yield and consistency of the final product.
2.Quality: Permanent mold casting produces parts with excellent surface finishes and precise dimensions, reducing the need for extensive machining. Our in-house solidification analysis in virtual reality anticipates and mitigates defects from day one, ensuring that quality is built into the process.
3.Cost-Effectiveness: While initial tooling costs may be higher, long-term savings from reduced waste and faster production often outweigh these costs. The permanent mold casting method offers cost-effective tooling that is approximately one-tenth the cost of pressure die cast tooling, making it a financially viable option for many manufacturers.
4.Durability and Longevity: The permanent nature of metal molds ensures that manufacturers can undertake large production runs without the need for constant mold replacement. Unlike sand molds that deteriorate with each casting cycle, permanent molds can withstand tens of thousands of casting cycles when properly maintained.
This longevity translates into significant cost savings over the production lifecycle. Additionally, the consistent performance of permanent molds across multiple casting cycles ensures that each part maintains uniform quality characteristics – essential for applications where batch consistency is critical. Industries such as aerospace and automotive rely heavily on this consistency to maintain quality control standards and meet stringent regulatory requirements.
The thermal stability of metal molds also contributes to predictable cooling rates, which directly impact the mechanical properties of the final product, ensuring that parts meet specifications with minimal variation. When comparing the advantages and disadvantages of different metal processing methods, permanent mold casting often emerges as a leading choice for projects requiring high-volume production with stringent quality standards. The strength-to-weight ratios achieved through this method make it particularly suitable for industries like aerospace and automotive, where performance is critical.
What are the Types of Molds in Casting?
In casting, two main types of molds are commonly used:
1.Permanent Molds: Made from metal, these molds can be reused multiple times, making them ideal for high-volume production. The durability of permanent molds contributes to their consistent output quality, essential for applications demanding high precision.
2.Sand Molds: Made from a mixture of sand and binder, these molds are typically used for lower volume runs or complex shapes that may not be feasible with permanent molds. While sand molds can accommodate intricate designs, they often require more finishing work, which can increase overall production time and costs.
3.Hybrid Approaches and Modern Innovations: Contemporary manufacturing increasingly employs hybrid approaches that combine the strengths of both mold types. Some manufacturers utilize temporary metal inserts within sand molds to achieve higher precision in critical areas while maintaining the flexibility of sand casting. Furthermore, the integration of advanced materials such as shell cores within permanent molds has expanded the possibilities for casting intricate internal geometries.
These innovations allow manufacturers to optimize costs while maintaining quality standards. The development of semi-permanent molds, which incorporate replaceable core elements, represents another advancement in casting technology. These solutions provide manufacturers with greater flexibility in production scheduling and part design customization, bridging the gap between the efficiency of permanent molds and the design adaptability of sand casting methods.
Each mold type has specific uses, with permanent molds being favored for their durability and consistent output quality. The tooling design and manufacturing capabilities at Procast ensure our molds are optimized for performance, providing our clients with reliable solutions tailored to their unique manufacturing needs. Understanding the nuances of permanent mold casting and its applications can significantly impact manufacturing strategies. By leveraging advanced technologies like SolidWorks CAD and GibbsCAM, we ensure that our clients benefit from cutting-edge design and production methodologies, further enhancing the advantages of permanent mold casting.
Materials Used in Permanent Mold Casting
Permanent mold casting is a precision casting process that utilizes reusable metal molds to produce high-quality, intricate parts. The selection of materials for both the mold and the casting is critical to achieving the desired mechanical properties and surface finishes. Understanding the material requirements for permanent mold vs die casting is essential, as each process imposes different thermal and mechanical demands on both mold and casting materials.
Mold Materials:Steel Alloys: Commonly used for their durability and ability to withstand repeated use.
Cast Iron: Offers good thermal conductivity and is cost-effective for certain applications.
|
Casting Materials:Aluminum Alloys: Renowned for their lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace components.
Zinc Alloys: Provide good strength and are often used for intricate designs due to their fluidity during casting.
Magnesium Alloys: Known for their low density and high strength-to-weight ratio, suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical.
|
Advanced Material Considerations:
The selection of casting materials has evolved significantly with technological advancements. Copper alloys, for instance, are increasingly used in applications requiring exceptional thermal conductivity, such as heat exchangers and specialized electrical components.
These alloys offer superior performance in high-temperature applications while maintaining structural integrity. Titanium alloys, though more expensive, are employed in aerospace applications where weight reduction and strength are paramount. The aerospace industry particularly favors titanium for components exposed to extreme environmental conditions.
Moreover, the development of composite casting materials that incorporate reinforcing particles has opened new possibilities for achieving customized mechanical properties. These advanced materials allow manufacturers to fine-tune the strength-to-weight ratios of their products, meeting increasingly demanding performance specifications.
When selecting casting materials, manufacturers must also consider environmental factors such as corrosion resistance, thermal expansion coefficients, and compatibility with secondary processing treatments like anodizing or heat treatment. The choice of materials is influenced by factors such as the desired mechanical properties, thermal conductivity, and the specific requirements of the end-use application.
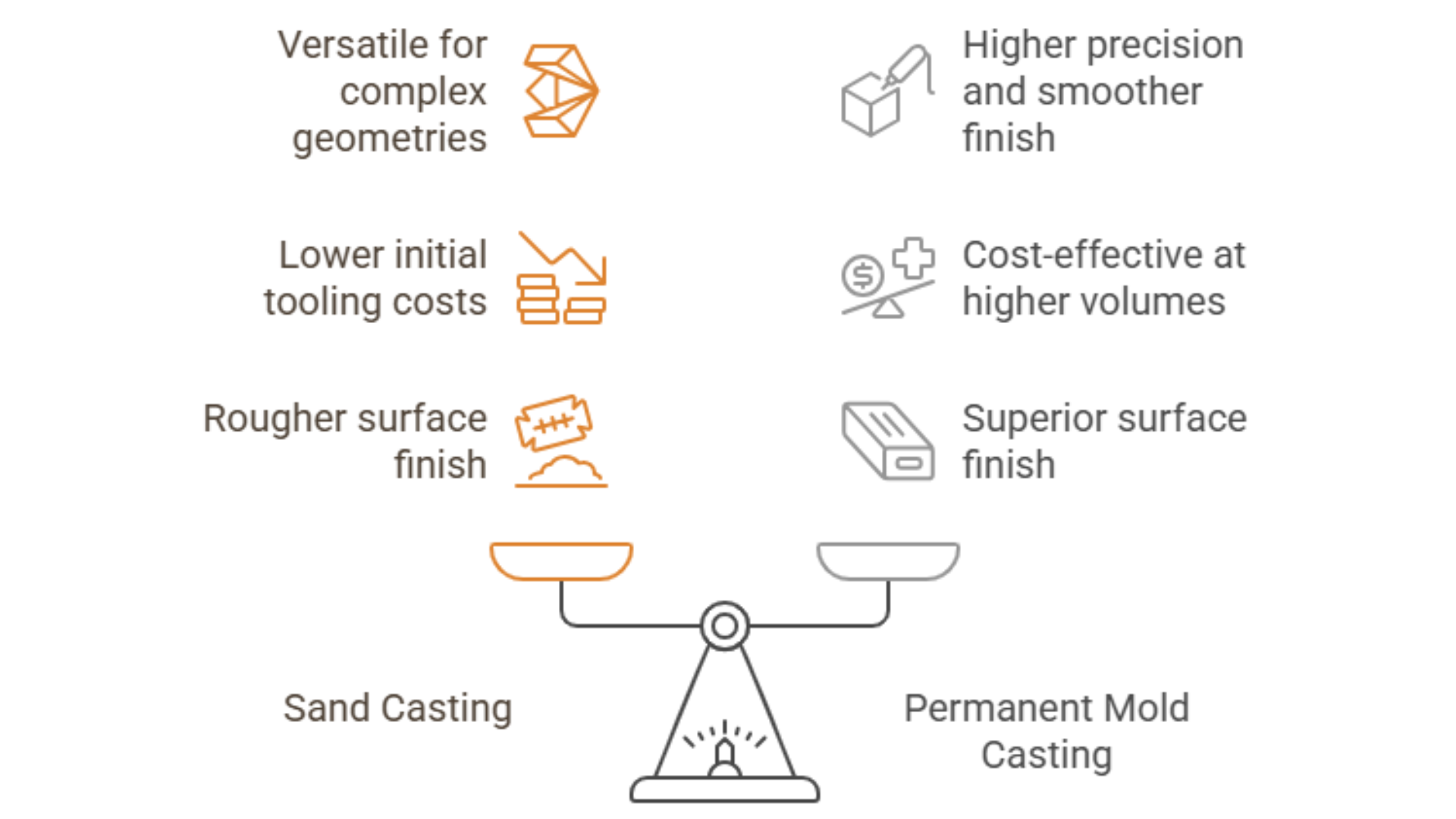
Differences Between Sand Casting and Permanent Mold Casting
Understanding the distinctions between sand casting and the permanent mold casting process is essential for selecting the appropriate method for a given project.
Venting in the Permanent Mold Process
Effective venting is crucial in permanent mold casting to ensure the removal of gases and prevent defects such as air pockets or blowholes.
Venting Methods:
| Venting Channels: Incorporating channels in the mold design allows gases to escape during the pouring of molten metal. | Strategic Mold Design: Positioning vents at high points in the mold facilitates the escape of gases, reducing the risk of defects. |
Proper venting not only enhances the quality of the casting but also improves the efficiency of the casting process.
Quality Control and Inspection in Permanent Mold Casting
Modern permanent mold casting operations employ sophisticated quality control measures to ensure defect-free production. Non-destructive testing methods, including X-ray radiography and ultrasonic inspection, are routinely used to detect internal defects such as porosity or inclusions. These inspection protocols are often integrated into the production workflow, allowing real-time monitoring and immediate corrective actions.
Additionally, dimensional verification using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) ensures that parts meet specified tolerances. The combination of preventive measures during design and simulation phases with rigorous post-casting inspection creates a comprehensive quality assurance framework that minimizes waste and ensures consistent delivery of high-quality components to end customers.
Cost Implications of Permanent Mold Casting
The cost of permanent mold casting is influenced by several factors:
1.Complexity of Design: Intricate designs may require more sophisticated mold manufacturing techniques, increasing costs.
2.Material Selection: The choice of materials for both the mold and the casting affects the overall cost.
3.Production Volume: Higher production volumes can amortize the initial tooling investment, reducing the cost per unit.
4.Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs: Regular maintenance of permanent molds is essential to maximize their operational lifespan and ensure consistent casting quality. Molds require periodic cleaning, surface treatment, and occasional refurbishment to maintain optimal performance. Preventive maintenance programs can significantly extend mold life, often doubling or tripling the number of casting cycles before replacement becomes necessary.
Manufacturers must also consider the cost of mold storage and handling equipment, as permanent molds require careful management to prevent damage. When properly maintained, these molds deliver exceptional return on investment through years of reliable service, making them economically superior for sustained production operations despite higher upfront costs compared to expendable mold alternatives.
While specific costs can vary, a rough estimate for permanent molds can range from thousands to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on these variables. When evaluating the best casting method for your project, it’s essential to consult with aluminum casting companies to get tailored quotes based on your specific requirements.
When evaluating the best casting method for your project, it’s essential to consult with aluminum casting companies to get tailored quotes based on your specific requirements. It’s essential to consult with aluminum casting companies to get tailored quotes based on your specific requirements.
Conclusion
The selection of materials, understanding the differences between casting methods and cost evaluation are all critical considerations in the permanent mold casting process. By leveraging advanced techniques and utilizing extensive quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure high-quality, defect-free parts tailored to specific needs.
Discover the advantages of Permanent Mold Aluminum Casting at Procast Technologies for your next project! Dive deeper into our comprehensive guide and unlock expert insights, tips, and best practices to elevate your manufacturing process.
