Mastering high-quality mold creation is essential for achieving precision and repeatability in aluminum casting. The choice between mold types determines the efficiency, accuracy, and final mechanical properties of the finished component. Understanding the various manufacturing processes enables producers to select the method best suited for specific production volumes and design complexity.
This guide explains the two main types of casting molds, their characteristics, and the specific steps involved in making aluminum casting molds, including methods for achieving long-term production runs. The success of these processes depends heavily on solidification analysis, tooling design, and strict process control—all key factors in successful permanent mold aluminum casting. The focus here is on the advantages and disadvantages of permanent mold casting and its impact on product development.
What are the two types of molds in casting?
The two fundamental types of molds in casting are permanent molds and expendable molds.
Expendable molds, such as those used in sand casting, are destroyed after each use to remove the solidified metal. Permanent molds, on the other hand, are made from durable materials such as high-strength steel, graphite, or cast iron and are designed for repeated use. When selecting aluminum casting mold materials, thermal resistance is a top priority, as the molds must withstand the extreme heat and stress of molten aluminum.
Aluminum is typically poured at temperatures above 1100°F after cleaning, adding alloying elements, and refining the grain structure before entering the casting table. Permanent molds consistently produce components with superior dimensional accuracy and finer surface finishes compared to expendable molds.
| Mold Type | Material Example | Reusability | Typical Surface Finish |
|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent | Steel, Cast Iron, H13 | High, Multi-Cycle | Superior, Fine |
| Expendable | Sand, Plaster | Low, Single-Use | Rougher |
Is die casting a permanent mold?
Die casting is a type of permanent mold process because the mold, called a die, is made from durable steel or similar material and can be reused thousands of times. Die casting involves injecting molten aluminum under high pressure into the mold cavity, resulting in rapid solidification. However, traditional die casting has limitations when creating complex internal shapes.
The semi-permanent mold process overcomes these limitations by using sand cores to create intricate internal features that pressure die casting cannot achieve. Specialized aluminum mold casting methods, such as static or tilt-pour permanent mold techniques, ensure exceptional quality, consistency, and desired microstructure in the finished component.
Which casting processes utilize permanent molds?
Several processes rely on permanent mold tooling, including gravity die casting, low-pressure die casting, and dedicated permanent mold aluminum casting used by specialized manufacturers. Permanent mold methods provide a significant advantage over single-use systems like sand or investment casting.
Permanent mold casting is highly efficient for medium production volumes (typically 500 to 50,000 pieces per year) and offers optimal cost-efficiency. The technique allows precise control over the alloy’s microstructure, maximizing mechanical strength and integrity. Since aluminum is sensitive to porosity, proper molten metal treatment—including hydrogen removal—is essential to maintain quality.
How to make aluminum casting molds?
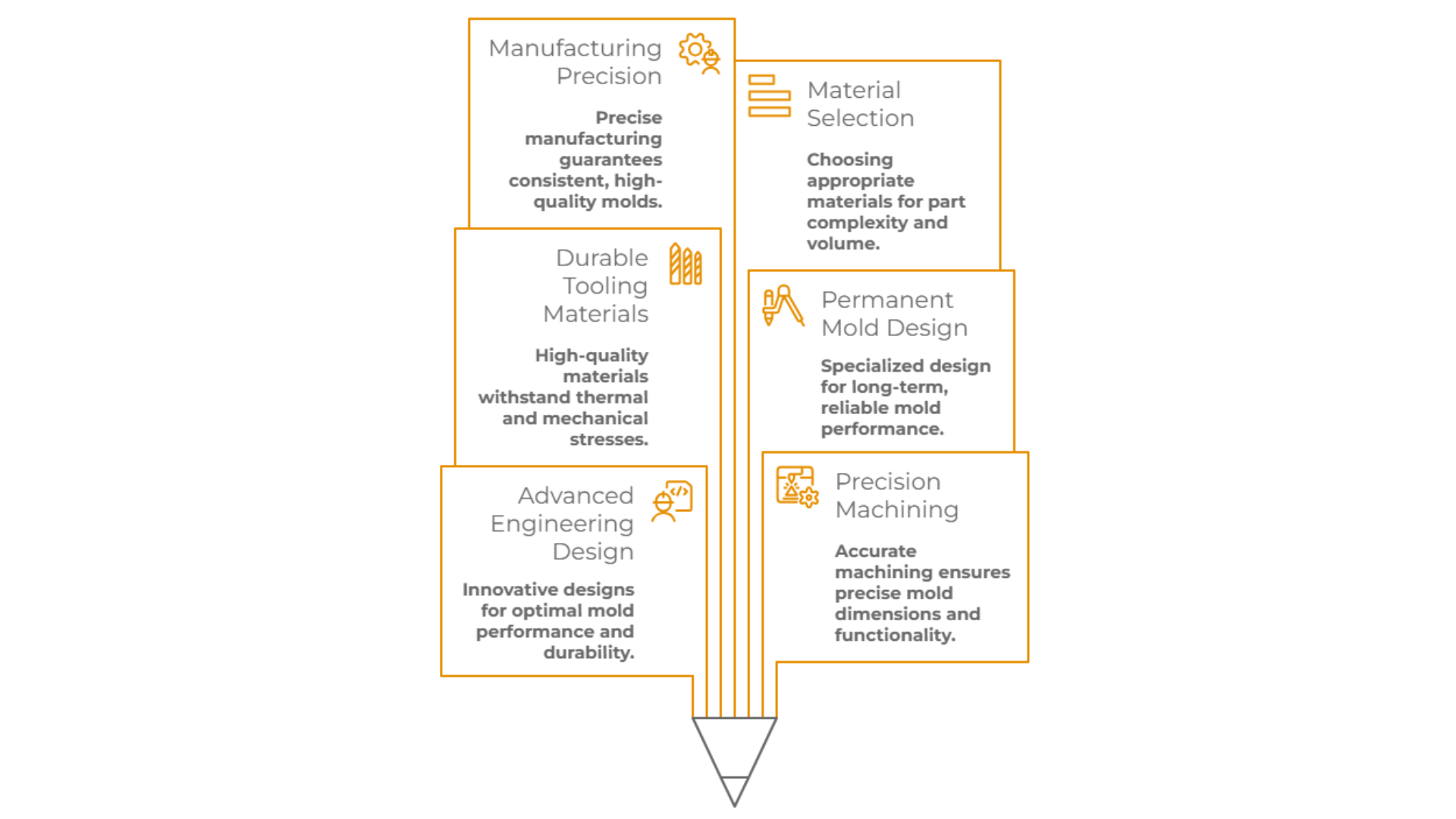
Building aluminum casting molds requires advanced engineering design, precision machining, and durable tooling materials capable of withstanding repeated thermal and mechanical stress. The design process includes solidification analysis to optimize mold structure and ensure consistently high results.
Creating a permanent mold for aluminum casting is key to achieving long-term production efficiency and reliable quality. Unlike disposable sand molds, aluminum permanent molds demand specialized tooling design and manufacturing precision. The selection of mold materials depends on part complexity and the expected production volume.
Solidification analysis should be integrated early in the process to optimize mold design and ensure consistent, high-quality outcomes. This methodical approach is essential for producing permanent aluminum casting molds that deliver dimensional stability and reliable surface finishes over time.
How to make a permanent mold for aluminum casting?
- To create a successful permanent mold for aluminum casting, manufacturers must prioritize durability by using materials such as tool steel or cast iron and ensuring high-precision features that extend mold life. These molds must withstand the thermal cycling of molten aluminum without cracking or warping.
- When designing the mold cavity, include a minimum draft angle of about 3° for permanent mold tooling. Consistency and reliability in permanent molds play a major role in maintaining quality control for medium to high production volumes.
- In aluminum alloys, differences in microstructure occur between fast- and slow-quenched areas, emphasizing the importance of mold design in cooling control.
Conclusion
Creating high-performance aluminum casting molds depends on selecting durable materials and applying expert engineering to produce a precise, interconnected mold system. This approach replaces disposable tooling with permanent molds that drive consistency, quality, and efficiency in long production runs. Maintaining tight process control and optimizing mold design ensures components meet strict mechanical requirements and deliver repeatable results.
Ready to enhance your production with the precision of permanent mold aluminum casting here at Procast Technologies? Subscribe to our blog for expert insights, tips, and the latest industry trends to improve your design and manufacturing strategies.
